Entity Framework Bulk Merge (Upsert, Insert + Update)
The BulkMerge method lets you merge entities using your EF Core model into your database. This kind of merge operation is often called “Upsert,” “Add or Update,” or “Insert or Update.” There is currently no direct equivalent to BulkMerge built into EF Core.
When you perform a bulk merge, it behaves as follows:
- Rows that match the entity key are UPDATED.
- Rows that do not match any existing record are INSERTED.
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; // Easy to use context.BulkMerge(customers); // Easy to customize context.BulkMerge(customers, options => options.IncludeGraph = true);
Online Example (EF Core) | Online Example (EF6)
🔑 Key Benefits
One of the main reasons people use our Bulk Merge is to perform add or update (upsert) operations exactly the way they want. You get full control over how rows are matched, which values are inserted, and how updates are applied — all with exceptional performance.
- ✅ Add or update the way you want: Define custom keys, control which properties to insert or update, and apply conditions.
- ✅ Extremely fast: Handle thousands or millions of upserts in seconds.
- ✅ No need to load entities: Save resources by working directly with your data, no tracking required.
- ✅ Flexible with hundreds of options: Customize behavior to fit your rules — from conditional updates to advanced key matching.
🔍 What is supported?
Our library supports all the common scenarios — and almost everything you can do with EF Core and EF6!
- ✅ The latest Entity Framework Core version: EF Core 10
- ✅ All previous EF Core versions: EF Core 2 to 9
- ✅ All Entity Framework versions: EF6, EF5, EF4, and EF Classic
- ✅ All major database providers: SQL Server, SQL Azure, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, SQLite, and Oracle
- ✅ All inheritance mapping strategies: TPC, TPH, and TPT
- ✅ Complex types / owned entity types
- ✅ Enums
- ✅ Value converters (EF Core)
- ✅ And much more — even shadow properties!
🚀 Performance Comparison
| Operations | 1,000 Entities | 2,000 Entities | 5,000 Entities |
|---|---|---|---|
| SaveChanges | 4,000 ms | Too long... | Way way too long... |
| BulkMerge | 80 ms | 110 ms | 170 ms |
Try it in EF Core | Try it in EF6
HINT:A lot of factors might affect the benchmark time such as index, column type, latency, throttling, etc.
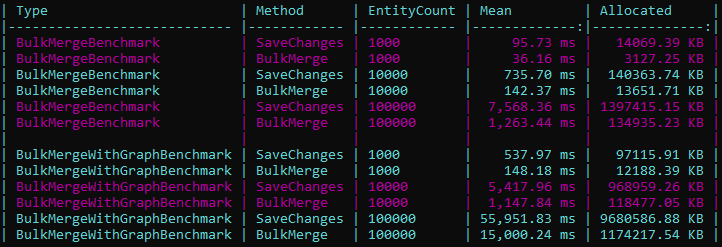
📊 Benchmark Results
The tables above give you a quick idea of the performance gains when using Bulk Merge.
But to give you a more complete picture, we also ran extensive benchmarks across all major database providers with BenchmarkDotNet.
👉 Explore detailed results:
- By provider (EF Core):
- By operation (EF Core):
Here’s an example chart for SQL Server – Bulk Merge comparing EF Core SaveChanges vs EF Extensions BulkMerge:
Scenarios
The BulkMerge method is fast but also flexible to let you handle various scenarios in Entity Framework such as:
- Merge and keep identity value
- Merge with custom key
- Merge and include/exclude properties
- Merge with related child entities (Include Graph)
- Merge with future action
- More scenarios
Advantages
- Easy to use
- Flexible
- Increase performance
- Increase application responsiveness
- Reduce database load
- Reduce database round-trips
Getting Started
Bulk Merge
The BulkMerge and BulkMergeAsync methods extend your DbContext to let you merge a large number of entities in your database.
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; context.BulkMerge(customers); context.BulkMergeAsync(customers, cancellationToken);
Try it in EF Core | Try it in EF6
Bulk Merge with options
The options parameter lets you use a lambda expression to customize the way entities are inserted or updated.
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; context.BulkMerge(customers, options => options.ColumnPrimaryKeyExpression = c => c.Code);
Try it in EF Core | Try it in EF6
Why BulkMerge is faster than SaveChanges?
Merging thousands of entities for a file importation is a typical scenario.
The AddOrUpdate method performs a database round-trip for every entity to check if it already exists. The DetectChanges method is also called for every entity which makes this method even slower (it's like using the Add method instead of AddRange).
The SaveChanges method performs one database round-trip for every entity to update.
So, if you need to merge 10,000 entities, 20,000 database round-trips will be performed + 10,000 DetectChanges calls which is INSANELY slow.
The BulkMerge in contrast requires the minimum number of database round-trips possible. For example, under the hood for SQL Server, a SqlBulkCopy is performed first in a temporary table, then a MERGE from the temporary table to the destination table is performed which is the fastest way available.
Real Life Scenarios
Merge and keep identity value
Your entity has an identity property, but you want to force to insert a specific value instead. The MergeKeepIdentity option allows you to keep the identity value of your entity.
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; context.BulkMerge(customers, options => options.MergeKeepIdentity = true);
Try it in EF Core | Try it in EF6
Merge and include/exclude properties
You want to merge your entities but only for specific properties.
ColumnInputExpression: This option lets you choose which properties to map.ColumnIgnoreExpression: This option lets you ignore properties that are auto-mapped.IgnoreOnMergeInsertExpression: This option lets you ignore properties only for theINSERTpart.IgnoreOnMergeUpdateExpression: This option lets you ignore properties only for theUPDATEpart.
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; context.BulkMerge(customers, options => options.ColumnInputExpression = c => new { c.CustomerID, c.Name} ); context.BulkMerge(customers, options => options.IgnoreOnMergeUpdateExpression = c => new { c.UpdatedDate } );
Try it in EF Core | Try it in EF6
Merge with custom key
You want to merge entities, but you don't have the primary key. The ColumnPrimaryKeyExpression lets you use as a key any property or combination of properties.
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; context.BulkMerge(customers, options => options.ColumnPrimaryKeyExpression = c => c.Code);
Try it in EF Core | Try it in EF6
Merge with related child entities (Include Graph)
You want to merge entities but also automatically merge related child entities.
IncludeGraph: This option lets you automatically merge all entities part of the graph.IncludeGraphBuilder: This option lets you customize how to merge entities for a specific type.
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; context.BulkMerge(invoices, options => options.IncludeGraph = true);
Try it in EF Core | Try it in EF6
Merge with future action
You want to merge entities, but you want to defer the execution.
By default, BulkMerge is an immediate operation. That means, it's executed as soon as you call the method.
FutureAction: This option lets you defer the execution of a Bulk Merge.
ExecuteFutureAction: This option triggers and executes all pending FutureAction.
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; context.FutureAction(x => x.BulkMerge(customers)); context.FutureAction(x => x.BulkMerge(invoices, options => options.IncludeGraph = true)); // ...code... context.ExecuteFutureAction();
Try it in EF Core | Try it in EF6
More scenarios
Hundreds of scenarios have been solved and are now supported.
The best way to ask for a special request or to find out if a solution for your scenario already exists is by contacting us: info@zzzprojects.com
Bulk Merge Options
Configuring Options
We already saw in previous article Configuring Options how to pass options to the BulkMerge method — but here’s a quick recap:
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; // Using a lambda expression (only works with one option) context.BulkMerge(list, options => options.MergeKeepIdentity = true); // Using a lambda expression with a body (works with one or multiple options) context.BulkMerge(list, options => { options.MergeKeepIdentity = true; options.ColumnPrimaryKeyExpression = x => new { x.ID }; }); // Using a `BulkOperationOption` instance var options = context.CreateBulkOptions<EntitySimple>(); options.MergeKeepIdentity = true; options.ColumnPrimaryKeyExpression = x => new { x.ID }; context.BulkMerge(list, options);
💡 Tip: Using a
BulkOperationOptioninstance is useful when you want to reuse the same configuration across multiple operations or keep your setup code more organized.
Common Options
- Bulk Merge Behavior
- IgnoreOnMergeInsert: Set to
falseif you want to ignore the insert phase part of the merge operation. - IgnoreOnMergeUpdate: Set to
falseif you want to ignore the update phase part of the merge operation. - MergeKeepIdentity: Set to
trueif you want to insert entities with their identity value. For SQL Server, the library will automatically handle theSET IDENTITY_INSERT [tableName] ONandSET IDENTITY_INSERT [tableName] OFFcommands. - MergeNotMatchedAndFormula: Specify a hardcoded SQL if you want to add custom logic to filter which rows should be inserted during the insert phase part of the merge operation.
- MergePrimaryKeyAndFormula: Specify a hardcoded SQL to include additional logic—along with the primary key—to check if the entity matches an existing row in the database. Only rows that also match the formula will be updated, all other rows will be inserted.
- MergeStagingTableFilterFormula: Specify a hardcoded SQL if you want to filter which rows should be merged (added or updated) using a staging table.
- IgnoreOnMergeInsert: Set to
- Coalesce Behavior
- OnMergeUpdateUseCoalesce: For each property, during the update phase of a merge operation, if the source value is
null, the destination value will stay unchanged. This behaves likeISNULL(StagingTable.ColumnName, DestinationTable.ColumnName)in SQL Server. - OnMergeUpdateUseCoalesceDestination: For each property, during the update phase of a merge operation, the destination value will only be updated if its current value in the database is
null. This behaves likeISNULL(DestinationTable.ColumnName, StagingTable.ColumnName)in SQL Server. - CoalesceOnMergeUpdateExpression: Use a lambda expression to specify which properties should apply the
OnUpdateUseCoalescelogic during the update phase of a merge operation. - CoalesceOnMergeUpdateNames: Use a list of strings to specify which properties should apply the
OnUpdateUseCoalescelogic during the update phase of a merge operation. - CoalesceDestinationOnMergeUpdateExpression: Use a lambda expression to specify which properties should apply the
OnUpdateUseCoalesceDestinationlogic during the update phase of a merge operation. - CoalesceDestinationOnMergeUpdateNames: Use a list of strings to specify which properties should apply the
OnUpdateUseCoalesceDestinationlogic during the update phase of a merge operation.
- OnMergeUpdateUseCoalesce: For each property, during the update phase of a merge operation, if the source value is
- Matched Behavior
- MergeMatchedAndFormula: After matching rows by primary key, you can specify an additional SQL condition to update only the rows that also satisfy this formula. Rows that do not satisfy the matched condition will be skipped entirely—they won’t be updated or inserted.
- MergeMatchedAndConditionExpression: After matching rows by primary key, you can specify additional properties using a lambda expression. All specified property values must match between the entity and the database for the row to be updated. Rows that do not satisfy the matched condition will be skipped entirely—they won’t be updated or inserted.
- MergeMatchedAndConditionNames: After matching rows by primary key, you can specify additional properties using a list of strings. All specified property values must match between the entity and the database for the row to be updated. Rows that do not satisfy the matched condition will be skipped entirely—they won’t be updated or inserted.
- MergeMatchedAndOneNotConditionExpression: After matching rows by primary key, you can specify additional properties using a lambda expression. At least one of the specified property values must differ between the entity and the database for the row to be updated. Rows that do not satisfy the matched condition will be skipped entirely—they won’t be updated or inserted.
- MergeMatchedAndOneNotConditionNames: After matching rows by primary key, you can specify additional properties using a list of strings. At least one of the specified property values must differ between the entity and the database for the row to be updated. Rows that do not satisfy the matched condition will be skipped entirely—they won’t be updated or inserted.
- IgnoreOnMergeMatchedAndConditionExpression: Use a lambda expression to select the properties you want to ignore. These properties will be excluded from the comparison performed by
MergeMatchedAndConditionExpression, and all other properties will be used for the match. - IgnoreOnMergeMatchedAndConditionNames: Use a list of strings to select the properties you want to ignore. These properties will be excluded from the comparison performed by
MergeMatchedAndConditionNames, and all other properties will be used for the match. - IgnoreOnMergeMatchedAndOneNotConditionExpression: Use a lambda expression to select the properties you want to ignore. These properties will be excluded from the comparison performed by
MergeMatchedAndOneNotConditionExpression, and all other properties will be used for the match. - IgnoreOnMergeMatchedAndOneNotConditionNames: Use a list of strings to select the properties you want to ignore. These properties will be excluded from the comparison performed by
MergeMatchedAndOneNotConditionNames, and all other properties will be used for the match.
- Behavior
- AutoTruncate: Set to
trueif you want string values to be automatically truncated to match the maximum database length before being merged (added or updated). This option is especially useful becauseSqlCommandandSqlBulkCopycan behave differently when a string is too long. (See Issue #333) - ExplicitValueResolutionMode: Specify how explicit values for columns (that aren’t usually expected to be set) should be handled. In EF Core, these values are always inserted. In EF Extensions, you need to tell how you want to handle them. Learn more here
- IncludeGraph: Set to
trueif you want to merge (add or update) both the main entities and their related entities. For example, if you pass a list ofOrderthat includesOrderItem, both will be merged. Be careful: if you want to apply specific options to a related entity type, you’ll need to configure them usingIncludeGraphBuilder. - IncludeGraphBuilder: Required only if
IncludeGraph = trueand you need to customize how a related entity type is merged. Use a lambda expression to control how each entity in the graph should be merged (added or updated) — for example, to define how child entities are linked to their parent or how IDs should be propagated.
- AutoTruncate: Set to
- Properties & Columns
- ColumnInputExpression: Choose which properties should be merged (added or updated) by using a lambda expression to select them. All other properties will be ignored.
- ColumnInputNames: Choose which properties should be merged (added or updated) by using a list of strings to select them. All other properties will be ignored.
- ColumnInputOutputExpression: Choose which properties should be merged (added or updated) and outputted by using a lambda expression to select them. All other properties will be ignored.
- ColumnInputOutputNames: Choose which properties should be merged (added or updated) and outputted by using a list of strings to select them. All other properties will be ignored.
- ColumnOutputExpression: Choose which properties should be outputted after the merge by using a lambda expression to select them.
- ColumnOutputNames: Choose which properties should be outputted after the merge by using a lambda expression to select them.
- ColumnPrimaryKeyExpression: Choose which properties should be part of the key by using a lambda expression. Only rows that match the key will be updated, all other rows will be inserted.
- ColumnPrimaryKeyNames: Choose which properties should be part of the key by using a list of strings. Only rows that match the key will be updated, all other rows will be inserted.
- OnMergeInsertInputExpression: Choose which properties using a lambda expression should be inserted during the insert phase of the merge operation. This option doesn't affect properties that will be updated.
- OnMergeInsertInputNames: Choose which properties using a list of strings should be inserted during the insert phase of the merge operation. This option doesn't affect properties that will be updated.
- OnMergeUpdateInputExpression: Choose which properties using a lambda expression should be updated during the updated phase of the merge operation. This option doesn't affect properties that will be inserted.
- OnMergeUpdateInputNames: Choose which properties using a list of strings should be updated during the updated phase of the merge operation. This option doesn't affect properties that will be inserted.
- IgnoreOnMergeInsertExpression: Choose which properties should be ignored by using a lambda expression to select them. All other properties will be inserted. This option does not affect the
UPDATEpart of the merge. - IgnoreOnMergeInsertNames: Choose which properties should be ignored by using a list of strings to select them. All other properties will be inserted. This option does not affect the
UPDATEpart of the merge. - IgnoreOnMergeUpdateExpression: Choose which properties should be ignored by using a lambda expression to select them. All other properties will be inserted. This option does not affect the
INSERTpart of the merge. - IgnoreOnMergeUpdateNames: Choose which properties should be ignored by using a list of strings to select them. All other properties will be inserted. This option does not affect the
INSERTpart of the merge.
- Optimization
- Batch: Customize the
BatchSize,BatchTimeout, andBatchDelayIntervalto improve performance and control how merged (add or update) entities are grouped and executed. - Hint: Use
QueryHintorTableHintSqlto apply SQL hints for additional performance tuning. - UseTableLock: Set to
trueto lock the destination table during the merge operation, which can improve performance by reducing row-level locks and avoiding lock escalation. This is especially useful when inserting a large number of rows.
- Batch: Customize the
- Providers Specific
- OracleMergeInsertTableHint: Gets or sets a "INSERT" hint (for BulkMerge) for ORACLE only.
- OracleMergeUpdateTableHint: Gets or sets a "UPDATE" hint (for BulkMerge) for ORACLE only.
- UsePostgreSqlInsertOnConflictDoNothing: Set to
trueif you want to silently ignore any conflict that would otherwise trigger a constraint violation error, such as a duplicate key. - UsePostgreSqlInsertOverridingSystemValue: Set to
trueif you want the values provided in theINSERTstatement (during theBulkMergeoperation) to take precedence over any default values defined at the database level for system columns. This is useful when you need to insert explicit values for columns like timestamps that are normally managed by the database. - UsePostgreSqlInsertOverridingUserValue: Set to
trueif you want the values in theINSERTstatement (during theBulkMergeoperation) to override any user-defined default values set at the database level. This is helpful when you want the application's data to take priority — especially during automated or bulk inserts. - UsePostgreOnMergeSqlInsertOnConflictDoUpdate: Set to
trueif you want to instead use a stragegy using the SQLON CONFLICT (key) DO UPDATEclause.
- General
- Audit: Track merged (add or update) entities by using the
UseAuditandAuditEntriesoptions. Learn more here - FutureAction: Batch multiple merge operations and execute them later using the
ExecuteFutureorExecuteFutureAsyncmethods. - Log: Log all executed SQL statements using the
Log,UseLogDump, andLogDumpoptions. Learn more here - RowsAffected: Use
UseRowsAffected = true, then accessResultInfo.RowsAffectedorResultInfo.RowsAffectedInsertedandResultInfo.RowsAffectedUpdatedto get the number of entities merged (added or updated). Learn more here
- Audit: Track merged (add or update) entities by using the
Troubleshooting
InsertIfNotExists doesn't work
This behavior is expected. The InsertIfNotExists option only applies to BulkInsert and BulkInsertOptimized.
The BulkMerge method already inserts new rows automatically when they don’t exist and updates existing ones — that’s its main purpose.
So, InsertIfNotExists doesn’t apply when using BulkMerge.
If you want to skip the insert part during a merge, you can use the following option instead:
options => options.IgnoreOnMergeInsert = true;
Lazy Loading + Include Graph (Update)
When lazy loading is enabled, using the IncludeGraph = true option will also trigger lazy loading and load all related entities. As a result, the entire graph may be updated, even if you didn’t intend to.
To avoid this behavior, you need to turn off lazy loading before retrieving your entities:
using (var context = new EntityContext()) { context.ChangeTracker.LazyLoadingEnabled = false; var invoices = context.Invoices.ToList(); // ...update invoice properties... context.BulkMerge(invoices, options => options.IncludeGraph = true); }
Conclusion
The BulkMerge method adds an "Add or Update" feature that you won’t find with the regular SaveChanges method. On top of that, it gives you full control over how you want to insert or update your entities using a variety of available options.
ZZZ Projects