Entity Framework Bulk Delete
The BulkDelete method lets you delete thousands of entities in EF Core. The biggest advantage of this method over the traditional approach is that you don’t need to fetch your entities from the database before deleting them (which doesn’t make much sense since you’re deleting them!).
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; // Easy to use context.BulkDelete(customers); // Easy to customize context.BulkDelete(customers, options => options.BatchSize = 100);
Online Example (EF Core) | Online Example (EF6)
Our library also offers several other ways to delete your entities even more easily and quickly:
🔑 Key Benefits
One of the main reasons people use our Bulk Delete is to delete entities exactly the way they want — without having to load them into memory or deal with tracking issues. You stay in control while getting top performance.
- ✅ Delete the way you want: Use custom keys, delete related entities (graph), or target specific conditions.
- ✅ Extremely fast: Delete thousands or millions of rows in seconds.
- ✅ No need to load entities: Avoid change tracking — delete directly from your data.
- ✅ Flexible with hundreds of options: Choose how relationships are handled, how keys are matched, and more.
🔍 What is supported?
Our library supports all the common scenarios — and almost everything you can do with EF Core and EF6!
- ✅ The latest Entity Framework Core version: EF Core 10
- ✅ All previous EF Core versions: EF Core 2 to 9
- ✅ All Entity Framework versions: EF6, EF5, EF4, and EF Classic
- ✅ All major database providers: SQL Server, SQL Azure, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, SQLite, and Oracle
- ✅ All inheritance mapping strategies: TPC, TPH, and TPT
- ✅ Complex types / owned entity types
- ✅ Enums
- ✅ Value converters (EF Core)
- ✅ And much more — even shadow properties!
🚀 Performance Comparison
| Operations | 1,000 Entities | 2,000 Entities | 5,000 Entities |
|---|---|---|---|
| SaveChanges | 1,200 ms | 2,400 ms | 6,000 ms |
| BulkDelete | 50 ms | 55 ms | 75 ms |
Try it in EF Core | Try it in EF6
HINT:A lot of factors might affect the benchmark time such as index, column type, latency, throttling, etc.
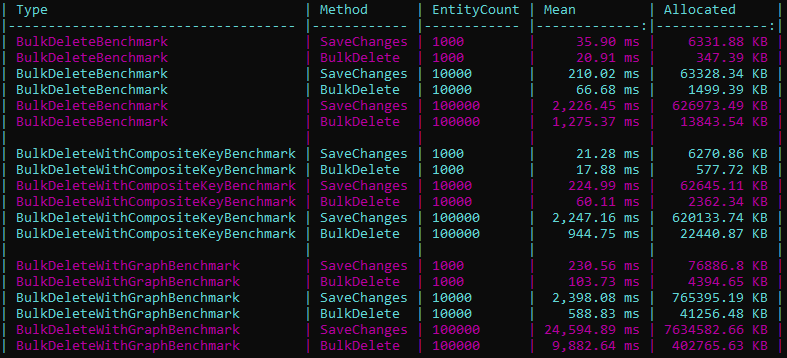
📊 Benchmark Results
The tables above give you a quick idea of the performance gains when using Bulk Delete.
But to give you a more complete picture, we also ran extensive benchmarks across all major database providers with BenchmarkDotNet.
👉 Explore detailed results:
- By provider (EF Core):
- By operation (EF Core):
Here’s an example chart for SQL Server – Bulk Delete comparing EF Core SaveChanges vs EF Extensions BulkDelete:
Scenarios
The BulkDelete method is fast but also flexible to let you handle various scenarios in Entity Framework such as:
Advantages
- Easy to use
- Flexible
- Increase performance
- Increase application responsiveness
- Reduce database load
- Reduce database round-trips
Getting Started
Bulk Delete
The BulkDelete and BulkDeleteAsync methods extend your DbContext to let you delete a large number of entities in your database.
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; context.BulkDelete(customers); context.BulkDeleteAsync(customers, cancellationToken);
Try it in EF Core | Try it in EF6
Bulk Delete with options
The options parameter lets you use a lambda expression to customize the way entities are deleted.
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; context.BulkDelete(customers, options => options.BatchSize = 100);
Try it in EF Core | Try it in EF6
Why BulkDelete is faster than SaveChanges?
Deleting thousands of entities for a file importation is a typical scenario.
The SaveChanges method makes it quite impossible to handle this kind of situation due to the number of database round-trips required. The SaveChanges performs one database round-trip for every entity to delete. So, if you need to delete 10,000 entities, 10,000 database round-trips will be performed which is INSANELY slow.
The BulkDelete by contrast requires the minimum number of database round-trips possible. For example, under the hood for SQL Server, a SqlBulkCopy is performed first in a temporary table, then a DELETE from the temporary table to the destination table is performed which is the fastest way available.
Real Life Scenarios
Delete with custom key
You want to delete entities, but you don't have the primary key. The ColumnPrimaryKeyExpression lets you use any property or combination of properties as a key.
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; context.BulkDelete(customers, options => options.ColumnPrimaryKeyExpression = c => c.Code);
Try it in EF Core | Try it in EF6
Delete with related child entities (Include Graph)
You want to delete entities but also automatically delete related child entities.
IncludeGraph: This option lets you automatically delete all entities part of the graph.IncludeGraphBuilder: This option lets you customize how to delete entities for a specific type.
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; context.BulkDelete(invoices, options => options.IncludeGraph = true);
NOTE: Only supported in EF Core 3+
Delete with future action
You want to delete entities, but you want to defer the execution.
By default, BulkDelete is an immediate operation. That means, it's executed as soon as you call the method.
FutureAction: This option lets you defer the execution of a Bulk Delete.
ExecuteFutureAction: This option triggers and executes all pending FutureAction.
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; context.FutureAction(x => x.BulkDelete(customers1)); context.FutureAction(x => x.BulkDelete(customers2)); // ...code... context.ExecuteFutureAction();
Try it in EF Core | Try it in EF6
More scenarios
Hundreds of scenarios have been solved and are now supported.
The best way to ask for a special request or to find out if a solution for your scenario already exists is by contacting us: info@zzzprojects.com
Bulk Delete Options
Configuring Options
We already saw in previous article Configuring Options how to pass options to the BulkDelete method — but here’s a quick recap:
// @nuget: Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.EFCore using Z.EntityFramework.Extensions; // Using a lambda expression (only works with one option) context.BulkDelete(list, options => options.IncludeGraph = true); // Using a lambda expression with a body (works with one or multiple options) context.BulkDelete(list, options => { options.IncludeGraph = true; options.ColumnPrimaryKeyExpression = x => new { x.ID }; }); // Using a `BulkOperationOption` instance var options = context.CreateBulkOptions<EntitySimple>(); options.IncludeGraph = true; options.ColumnPrimaryKeyExpression = x => new { x.ID }; context.BulkDelete(list, options);
💡 Tip: Using a
BulkOperationOptioninstance is useful when you want to reuse the same configuration across multiple operations or keep your setup code more organized.
Common Options
- Bulk Delete Behavior
- DeletePrimaryKeyAndFormula: Specify a hardcoded SQL to include additional logic—along with the primary key—to check if the entity matches an existing row in the database. Only rows that also match the formula will be deleted.
- DeleteStagingTableFilterFormula: Specify a hardcoded SQL if you want to filter which rows should be deleted using a staging table.
- Matched Behavior
- DeleteMatchedAndFormula: After matching rows by primary key, you can specify an additional SQL condition to delete only the rows that also satisfy this formula.
- DeleteMatchedAndConditionExpression: After matching rows by primary key, you can specify additional properties using a lambda expression. All specified property values must match between the entity and the database for the row to be deleted.
- DeleteMatchedAndConditionNames: After matching rows by primary key, you can specify additional properties using a list of strings. All specified property values must match between the entity and the database for the row to be deleted.
- DeleteMatchedAndOneNotConditionExpression: After matching rows by primary key, you can specify additional properties using a lambda expression. At least one of the specified property values must differ between the entity and the database for the row to be deleted.
- DeleteMatchedAndOneNotConditionNames: After matching rows by primary key, you can specify additional properties using a list of strings. At least one of the specified property values must differ between the entity and the database for the row to be deleted.
- IgnoreOnDeleteMatchedAndConditionExpression: Use a lambda expression to select the properties you want to ignore. These properties will be excluded from the comparison performed by
DeleteMatchedAndConditionExpression, and all other properties will be used for the match. - IgnoreOnDeleteMatchedAndConditionNames: Use a list of strings to select the properties you want to ignore. These properties will be excluded from the comparison performed by
DeleteMatchedAndConditionNames, and all other properties will be used for the match. - IgnoreOnDeleteMatchedAndOneNotConditionExpression: Use a lambda expression to select the properties you want to ignore. These properties will be excluded from the comparison performed by
DeleteMatchedAndOneNotConditionExpression, and all other properties will be used for the match. - IgnoreOnDeleteMatchedAndOneNotConditionNames: Use a list of strings to select the properties you want to ignore. These properties will be excluded from the comparison performed by
DeleteMatchedAndOneNotConditionNames, and all other properties will be used for the match.
- Behavior
- IncludeGraph: Set to
trueif you want to delete both the main entities and their related entities. For example, if you pass a list ofOrderthat includesOrderItem, both will be deleted. Be careful: if you want to apply specific options to a related entity type, you’ll need to configure them usingIncludeGraphBuilder. Only compatible with EF Core - IncludeGraphBuilder: Required only if
IncludeGraph = trueand you need to customize how a related entity type is deleted. Use a lambda expression to control how each entity in the graph should be deleted.
- IncludeGraph: Set to
- Properties & Columns
- ColumnPrimaryKeyExpression: Choose which properties should be part of the key by using a lambda expression. Only rows that match the key will be deleted.
- ColumnPrimaryKeyNames: Choose which properties should be part of the key by using a list of strings. Only rows that match the key will be deleted.
- Optimization
- Batch: Customize the
BatchSize,BatchTimeout, andBatchDelayIntervalto improve performance and control how deleted entities are grouped and executed. - Hint: Use
QueryHintorTableHintSqlto apply SQL hints for additional performance tuning. - UseTableLock: Set to
trueto lock the destination table during the delete operation, which can improve performance by reducing row-level locks and avoiding lock escalation. This is especially useful when inserting a large number of rows.
- Batch: Customize the
- Providers Specific
- OracleDeleteTableHint: Gets or sets a "DELETE" hint (for BulkDelete) for ORACLE only.
- General
- Audit: Track deleted entities by using the
UseAuditandAuditEntriesoptions. Learn more here - FutureAction: Batch multiple delete operations and execute them later using the
ExecuteFutureorExecuteFutureAsyncmethods. - Log: Log all executed SQL statements using the
Log,UseLogDump, andLogDumpoptions. Learn more here - RowsAffected: Use
UseRowsAffected = true, then accessResultInfo.RowsAffectedorResultInfo.RowsAffectedDeletedto get the number of entities deleted. Learn more here
- Audit: Track deleted entities by using the
Troubleshooting
Lazy Loading + Include Graph
When lazy loading is enabled, using the IncludeGraph = true option will also trigger lazy loading and load all related entities. As a result, the entire graph may be deleted.
To avoid this behavior, you need to turn off lazy loading before retrieving your entities:
using (var context = new EntityContext()) { context.ChangeTracker.LazyLoadingEnabled = false; var invoices = context.Invoices.ToList(); context.BulkDelete(invoices, options => options.IncludeGraph = true); }
Conclusion
The BulkDelete method is very powerful. One of its biggest benefits is that you don’t need to use the change tracker or retrieve your entities before deleting them (which often doesn’t make much sense anyway). The major benefit is the performance gain—but you can also delete using a custom key or even delete an entire entity graph.
Perfect when you want to delete thousands of rows fast—without slowing down your app.
ZZZ Projects