EF6 - MySql Provider
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) and it is known for its quick processing, proven reliability, ease and flexibility of use.
- It is a database system used on the web and is ideal for both small and large applications.
- It is an essential part of almost every open source PHP application.
Install EFE
Let's create a new application using the Console App (.NET Framework) template and install Z.EntityFramework.Extensions.
Entity Framework Extensions (EFE) library is available as a NuGet package and you can install it using NuGet Package Manager.
In the Package Manager Console window, enter the following command.
PM> Install-Package Z.EntityFramework.Extensions
You can also install EFE by right-clicking on your project in Solution Explorer and selecting Manage NuGet Packages....
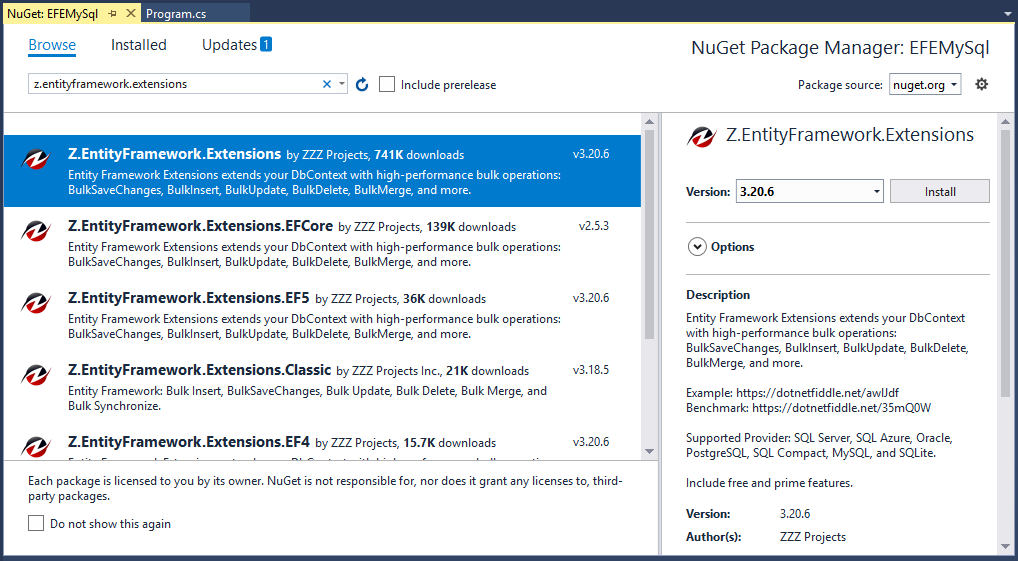
Search for Z.EntityFramework.Extensions and install the latest version by pressing the install button.
Register EF Provider
EF providers can be registered using either code-based configuration or in the application's config file. Install the MySql.Data.Entity NuGet package to add this reference automatically within app.config or web.config file during the installation.
PM> Install-Package MySql.Data.Entity
Let's open the App.config file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <configuration> <configSections> <section name="entityFramework" type="System.Data.Entity.Internal.ConfigFile.EntityFrameworkSection, EntityFramework, Version=6.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089" requirePermission="false" /> <!-- For more information on Entity Framework configuration, visit https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=237468 --></configSections> <startup> <supportedRuntime version="v4.0" sku=".NETFramework,Version=v4.7.2" /> </startup> <entityFramework> <defaultConnectionFactory type="System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.SqlConnectionFactory, EntityFramework" /> <providers> <provider invariantName="System.Data.SqlClient" type="System.Data.Entity.SqlServer.SqlProviderServices, EntityFramework.SqlServer" /> <provider invariantName="MySql.Data.MySqlClient" type="MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlProviderServices, MySql.Data.Entity.EF6, Version=6.10.8.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=c5687fc88969c44d"/> </providers> </entityFramework> </configuration>
Note that often if the EF provider is installed from NuGet, then the NuGet package will automatically add this registration to the config file.
- The invariantName in this registration is the same invariant name used to identify an ADO.NET provider. The invariant name
MySql.Data.MySqlClientis for MySql. - The type in this registration is the assembly-qualified name of the provider type that derives from
MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlProviderServices. For example, the stringMySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlProviderServices, MySql.Data.Entity.EF6, Version=6.10.8.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=c5687fc88969c44dhere is used for MySql.
Configuration
Set the new DbConfiguration class for MySQL. This step is optional but highly recommended because it adds all the dependency resolvers for MySQL classes and this can be done in three ways.
- Add the
DbConfigurationTypeAttributeon the context class.
[DbConfigurationType(typeof(MySqlEFConfiguration))]
Call
DbConfiguration.SetConfiguration(new MySqlEFConfiguration())at the application startup.You can also set the
DbConfigurationtype in the configuration file.
<entityFramework codeConfigurationType="MySql.Data.Entity.MySqlEFConfiguration, MySql.Data.Entity.EF6">
You are now ready to start your application.
Create Data Model
The model is a collection of classes to interact with the database.
- A model stores data that is retrieved according to the commands from the Controller and displayed in the View.
- It can also be used to manipulate the data to implement the business logic.
To create a data model for our application, we will start with the following two entities.
public class Author { public int AuthorId { get; set; } public string FirstName { get; set; } public string LastName { get; set; } public DateTime BirthDate { get; set; } public List<Book> Books { get; set; } } public class Book { public int BookId { get; set; } public string Title { get; set; } public Author Author { get; set; } }
There's a one-to-many relationship between Author and Book entities. In other words, an author can write any number of books, and a book can be written by only one author.
Create Database Context
The database context class provides the main functionality to coordinate Entity Framework with a given data model.
- You create this class by deriving from the
System.Data.Entity.DbContextclass. - In your code, you specify which entities are included in the data model.
- You can also customize certain Entity Framework behaviors.
So, let's add a new BookStore class which will inherit the DbContext class.
//[DbConfigurationType(typeof(MySqlEFConfiguration))] public class BookStore : DbContext { public BookStore() : base("BookStoreContext") { } public DbSet<Author> Authors { get; set; } public DbSet<Book> Books { get; set; } }
This code creates a DbSet property for each entity set. In Entity Framework terminology, an entity set typically corresponds to a database table, and an entity corresponds to a row in the table.
Setup Database
The name of the connection string is passed into the constructor of the context class.
public BookStore() : base("BookStoreContext") { }
So, let's open the application App.config file and add a connectionStrings element.
<connectionStrings> <add name="BookStoreContext" connectionString="server=localhost;database=BookStoreDb;uid=root;password=;" providerName="MySql.Data.MySqlClient"/> </connectionStrings>
The above connection string specifies that Entity Framework will use a localhost database named BookStoreDb.
Now, we are done with the required classes, so let's add some author and book records to the database and then retrieve it.
using (var context = new BookStore()) { context.Database.Delete(); var authors = new List<Author> { new Author { FirstName ="Carson", LastName ="Alexander", BirthDate = DateTime.Parse("1985-09-01"), Books = new List<Book>() { new Book { Title = "Introduction to Machine Learning"}, new Book { Title = "Advanced Topics in Machine Learning"}, new Book { Title = "Introduction to Computing"} } }, new Author { FirstName ="Meredith", LastName ="Alonso", BirthDate = DateTime.Parse("1970-09-01"), Books = new List<Book>() { new Book { Title = "Introduction to Microeconomics"} } }, new Author { FirstName ="Arturo", LastName ="Anand", BirthDate = DateTime.Parse("1963-09-01"), Books = new List<Book>() { new Book { Title = "Calculus I"}, new Book { Title = "Calculus II"} } } }; //IncludeGraph allows you to INSERT/UPDATE/MERGE entities by including the child entities graph. context.BulkInsert(authors, options => options.IncludeGraph = true ); } using (var context = new BookStore()) { var list = context.Authors .Include(a => a.Books) .ToList(); foreach (var author in list) { Console.WriteLine(author.FirstName + " " + author.LastName); foreach (var book in author.Books) { Console.WriteLine("\t" + book.Title); } } }
If you run the application, you will see that authors and books are successfully inserted into the database.
ZZZ Projects